Machine learning for computational biology

We develop and apply machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) methods for the analysis of large biomedical datasets. For example, we work on interpretable deep learning to make machine learning more useful for biomedical research.
Machine learning has emerged as a versatile approach for predicting a wide range of biological phenomena. However, its utility for biological discovery has been limited, given that machine learning methods (including the popular and powerful deep neural networks) typically provide little insight into the biological mechanisms that underlie a successful prediction.
We have a long-standing interest in making machine-learning algorithms more interpretable and useful for biological discovery and biomedical applications. Most recently, we have proposed the concept of “knowledge-primed neural networks” for interpretable deep learning on gene-regulatory networks which allows us to infer the activity of key regulatory proteins from single-cell sequencing data, including signaling pathways and protein activity states that are normally hidden to sequencing-based methods.
The power of interpretable machine learning for advancing biomedical research is further illustrated by a series of studies in which we applied machine learning to patient cohorts, for example for time series modelling of the drug response in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and for the identification of drug new combinations for targeted therapy. Moreover, we successfully used machine learning to reconstruct normal and aberrant stem cell differentiation in the blood.
Publications

GPT-4 as a biomedical simulator
Schaefer M, Reichl S#, ter Horst R#, Nicolas AM, Krausgruber T, Piras F, Stepper P, Bock C*, Samwald M*
Computers in Biology and Medicine 178, 108796 (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108796
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)
Press release
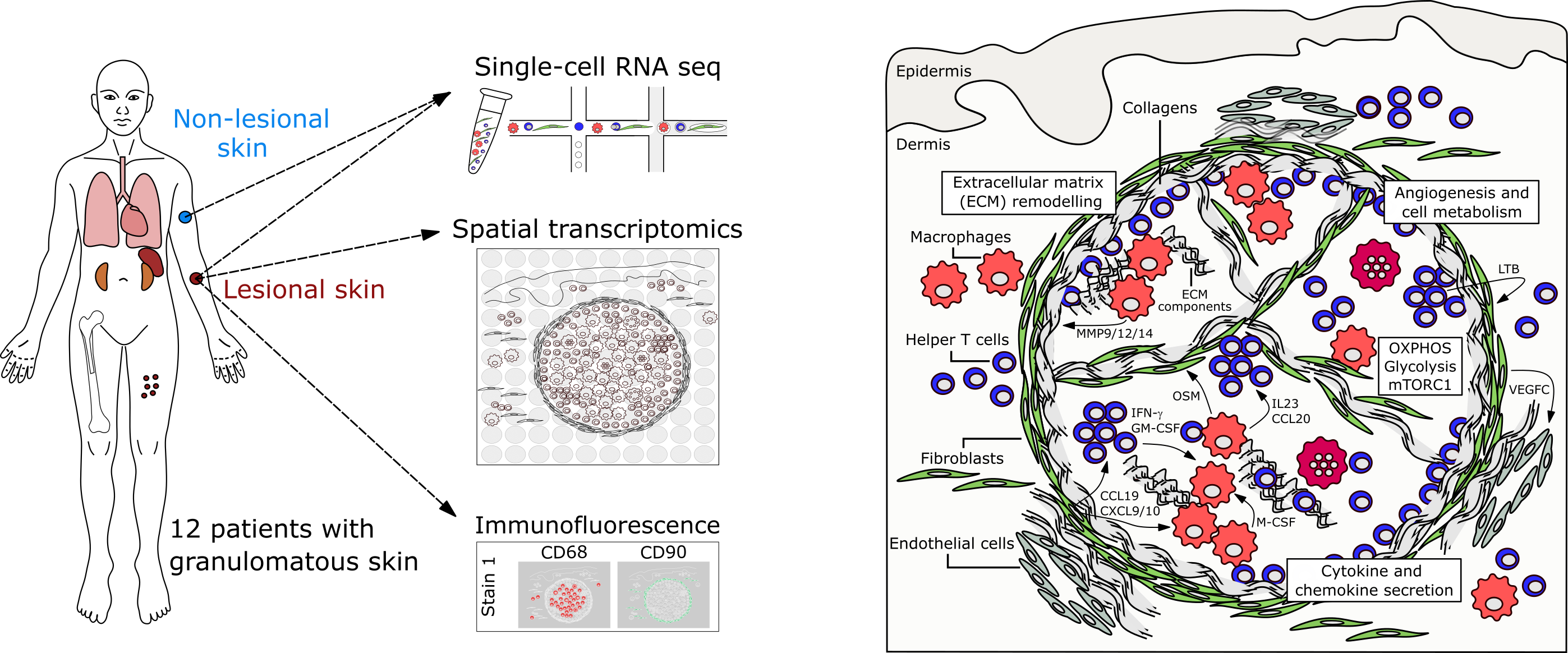
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveal aberrant lymphoid developmental programs driving granuloma formation
Krausgruber T, Redl A#, Barreca D#, Doberer K, Romanovskaia D, Dobnikar L, Guarini M, Unterluggauer L, Kleissl L, Atzmüller D, Mayerhofer C, Kopf A, Saluzzo S, Lim CX, Rexie P, Weichhart T, Bock C*, Stary G*
Immunity 56, 289-306 (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.014
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)
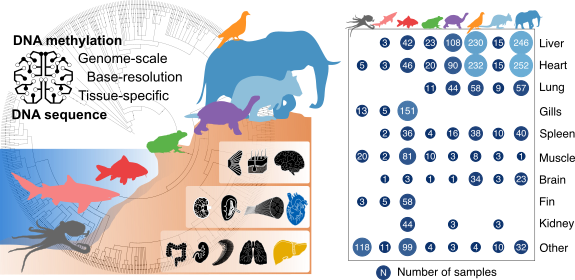
Comparative analysis of genome-scale, base-resolution DNA methylation profiles across 580 animal species
Klughammer J, Romanovskaia D#, Nemc A, Posautz A, Seid C, Linda, Schuster, Keinath M, Ramos JSL, Kosak L, Evankow A, Prinz D, Kirchberger S, Datlinger P, Fortelny N, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Kaja, Skjærven, Bergthaler A, Liedvogel M, Thaller D, Burger PA, Hermann0 M, Distel M, Distel DL, Kübber-Heiss A, Bock C*
Nature Communications 14, 232 (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34828-y
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Multimodal analysis of cell-free DNA whole-genome sequencing for pediatric cancers with low mutational burden
Peneder P, Stutz AM, Surdez D, Krumbholz M, Semper S, Chicard M, Sheffield NC, Pierron G, Lapouble E, Totzl M, Erguner B, Barreca D, Rendeiro AF, Agaimy A, Boztug H, Engstler G, Dworzak M, Bernkopf M, Taschner-Mandl S, Ambros IM, Myklebost O, Marec-Berard P, Burchill SA, Brennan B, Strauss SJ, Whelan J, Schleiermacher G, Schaefer C, Dirksen U, Hutter C, Boye K, Ambros PF, Delattre O, Metzler M, Bock C, Tomazou EM
Nature Communications 12, 3230 (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23445-w
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Knowledge-primed neural networks enable biologically interpretable deep learning on single-cell sequencing data
Fortelny N, Bock C
Genome Biology 21, 190 (2020). DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02100-5
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Chromatin mapping and single-cell immune profiling defines the temporal dynamics of ibrutinib drug response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Rendeiro AF*, Krausgruber T*, Fortelny N, Zhao F, Penz T, Farlik M, Schuster LC, Kuchler A, Tasnády S, Réti M, Zoltán M, Alpar D*, Bödör C*, Schmidl C*, Bock C*
Nature Communications 11, 577 (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-14081-6
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Combined chemosensitivity and chromatin profiling prioritizes drug combinations in CLL
Schmidl C*, Vladimer GI*, Rendeiro AF*, Schnabl S*, Krausgruber T, Taubert C, Krall N, Pemovska T, Araghi M, Snijder B, Hubmann R, Ringler A, Runggatscher K, Demirtas D, de la Fuente OL, Hilgarth M, Skrabs C, Porpaczy E, Gruber M, Hoermann G, Kubicek S, Staber PB, Shehata M*, Superti-Furga G*, Jäger U*, Bock C*
Nature Chemical Biology 15, 232-240 (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41589-018-0205-2
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

DNA methylation dynamics of human hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
Farlik M*, Halbritter F*, Müller F*, Choudry FA, Ebert P, Klughammer J, Farrow S, Santoro A, Ciaurro V, Mathur A, Uppal R, Stunnenberg HG, Ouwehand WH, Laurenti E, Lengauer T, Frontini M*, Bock C*
Cell Stem Cell 19, 808-822 (2016). DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.10.019
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Chromatin accessibility maps of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identify subtype-specific epigenome signatures and transcription regulatory networks
Rendeiro AF*, Schmidl C*, Strefford JC*, Walewska R, Davis Z, Farlik M, Oscier D, Bock C*
Nature Communications 7, 11938 (2016). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11938
Donwload PDF
Read online (without subscription)

Managing drug resistance in cancer: Lessons from HIV therapy
Bock C, Lengauer T
Nature Reviews Cancer 12, 494-501 (2012). DOI: 10.1038/nrc3297
Read online (without subscription)
Project website
Press release
* shared first or shared senior authorship